Monday, June 30, 2025
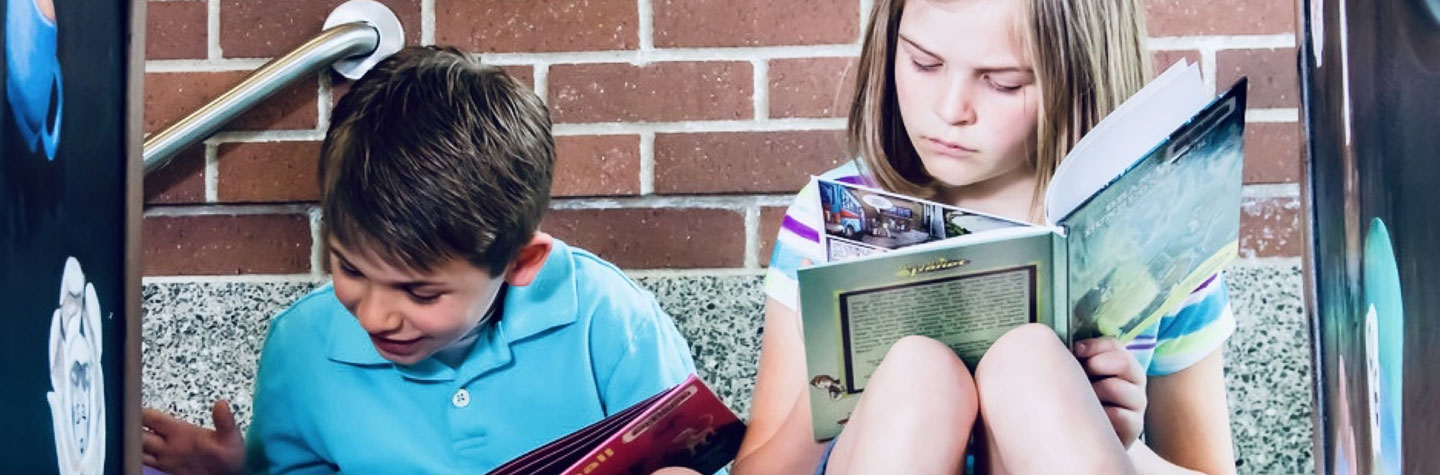

Many children struggle with learning how to read. Some kids can read well but choose not to read. For others, learning disabilities can make reading more challenging.
In today's world, kids have the option of many other activities that may keep them busy and distracted from reading. From after school activities and sports to the pull of devices, TV, and video games, reading for fun is often forgotten or avoided. Older kids might think reading is boring since they associate it with technical reading, like worksheets and textbooks in school.
There are plenty of things to try that can make reading more interesting and exciting to kids. Here are ten tips to try that might help motivate your infrequent reader:
1. Reconsider what counts as reading.
There are lots of ways to read, including listening! Audiobooks, radio shows, podcasts, oral stories — including sharing stories of your family and family history — are all great ways to explore literacy outside of written materials.
2. Let them choose what they want to read.
All reading is good reading. Be open to comics, manga, blogs, graphic novels, short stories, magazines, screenplays, picture books (even for big kids), song lyrics, books of world records and fun facts, profiles of musicians, artists and sports heroes, or gross-out science books. Visit your public library in person and online for a huge selection of reading material. Our expert staff would also be happy to help make recommendations based on your child’s reading preferences.
3. Avoid banning what they love to read.
From comic books with adult themes to serial tween romances, it’s natural for caregivers to be concerned about the content of their child’s books. But banning what they love can discourage reading. Instead, talk about why you think certain books are offensive and invite them to ask questions. Let your child recommend a book to you so you can read it and discuss the book together. Everyone has different tastes, which is part of the joy of being a reader.
Concerned about age-appropriate content? Look for an online booklist curated for your child’s age or interests. You can use the “advanced search” function in your library’s online catalogue to search by collection (i.e. Hindi, Biography), format (i.e. Graphic Novel) and Audience (i.e. teen).
4. Let your kids see you enjoy reading.
Nearly 60% of kids who are frequent readers have parents who read five to seven days per week, compared to only 15% of kids who are infrequent readers (Kids and Family Reading Report – Scholastic, 2017).
5. Read together as a family.
Make reading a memorable family event. Set aside regular time for reading, whether as a family or each person reading independently near each other. Children whose parents are involved with them in family literacy activities score ten points higher on standardized reading tests.
6. Read in your home language.
Children who learn to read in their first language have an easier time learning to read in a second language because they better understand the process of reading.
7. Try reading something funny!
Read dramatically, use costumes and accents, or read joke books to each other. Have fun when reading aloud together! Try not to focus on their mistakes and simply enjoy the book. These staff-recommended books will help you get your giggle on.
8. Relax.
When we enjoy something, we want to keep doing it — the same applies to reading. Try to make reading as relaxing as possible at home, especially if reading at school is stressful. Have a special snack or read in a special spot. If there’s a movie adaptation of the book, watch the movie together after you’ve finished the book and decide which you liked better.
9. Keep reading sessions short and simple.
Research shows that when students believe they can achieve a task, they are much more likely to persevere and overcome challenges. Parents can help build their child’s reading confidence by praising their effort rather than their outcomes. Use affirming language throughout the process to show that you enjoy seeing their efforts. Another strategy is to break reading into smaller parts, even just one paragraph at a time, so that success comes quickly and can be celebrated.
10. Find a role model for your reader.
Research shows that older boys read less than their female peers. Men that model reading to boys can have a positive influence, especially around a shared interest. Sports statistics, LEGO instructions, musician biographies, etc., all count as reading too!